How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that blends technical understanding with responsible piloting. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding the individual components and pre-flight checks to mastering advanced maneuvers and capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll explore essential safety regulations, troubleshoot common issues, and navigate the legal landscape of drone flying, ensuring you’re well-equipped for a successful and responsible flight experience.
We will cover everything from the basic mechanics of your drone and its components to advanced flight techniques and the legal considerations you need to be aware of. By the end of this guide, you will be confident in your ability to safely and responsibly operate your drone, capturing breathtaking aerial photography and videography along the way.
Drone Parts and Components
Understanding the individual components of a drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. Each part plays a vital role in the drone’s flight capabilities and overall performance. This section will detail the function of key components, explore different types of batteries and propellers, and provide a comparative overview of common specifications.
Drone Component Functions
A drone’s functionality relies on the coordinated operation of several key components. These include the propellers, motors, flight controller, battery, GPS, and camera.
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate thrust, enabling the drone to take off, hover, and maneuver. Different propeller designs affect flight characteristics.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers, converting electrical energy into mechanical rotation. Motor size and power directly impact flight performance.
- Flight Controller: This is the drone’s “brain,” processing data from various sensors and controlling the motors to maintain stability and execute pilot commands. It manages orientation, altitude, and other flight parameters.
- Battery: The battery provides power to all drone components. Battery capacity (mAh) and voltage (V) significantly impact flight time and performance.
- GPS: The Global Positioning System allows for precise location tracking, enabling features like Return-to-Home (RTH) and autonomous flight modes.
- Camera: The camera captures aerial photos and videos. Camera quality varies widely, impacting image resolution and features.
Drone Battery Types and Characteristics
Drone batteries are typically lithium polymer (LiPo) batteries, known for their high energy density. Different LiPo batteries have varying characteristics, affecting flight time and performance. Key characteristics include capacity (mAh), voltage (V), discharge rate (C), and cell count.
- Capacity (mAh): Indicates the battery’s energy storage capacity, directly related to flight time.
- Voltage (V): Determines the power output of the battery.
- Discharge Rate (C): Represents the maximum current the battery can safely deliver. Higher C ratings support more demanding flight maneuvers.
- Cell Count: Refers to the number of individual cells within the battery pack. A higher cell count generally results in a higher voltage.
Drone Propeller Types and Flight Performance
Drone propellers come in various sizes and designs, each impacting flight characteristics. Factors such as pitch, diameter, and material affect thrust, speed, and efficiency.
- Pitch: The angle of the propeller blade, influencing thrust and speed.
- Diameter: The size of the propeller, affecting lift and overall power.
- Material: Materials like plastic or carbon fiber influence durability and weight.
Common Drone Component Specifications
| Component | Specification 1 | Specification 2 | Specification 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Motor | KV Rating (RPM/V) | Power (Watts) | Weight (grams) |
| Battery | Capacity (mAh) | Voltage (V) | Discharge Rate (C) |
| Propeller | Diameter (inches) | Pitch (inches) | Material |
| Flight Controller | Processor | IMU Type | Firmware Version |
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is essential for safe and responsible drone operation. This involves inspecting the drone, checking battery levels, verifying GPS signal strength, and understanding local regulations. Ignoring these steps can lead to accidents or legal issues.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, carefully inspect the drone and its components to ensure everything is functioning correctly. This checklist helps prevent accidents and ensures a safe flight.
- Inspect the drone’s physical condition for any damage.
- Check the battery level and ensure it is fully charged.
- Verify the GPS signal strength and accuracy.
- Calibrate the drone’s sensors if necessary.
- Review local regulations and airspace restrictions.
- Check weather conditions and avoid flying in adverse weather.
- Select a safe and open flight area, away from obstacles and people.
Safety Regulations and Guidelines
Responsible drone piloting requires adherence to local and national regulations. These regulations often cover airspace restrictions, registration requirements, and operational limitations. Familiarizing yourself with these regulations is crucial for legal and safe drone operation.
- Airspace Restrictions: Many areas have restricted airspace, such as airports and military bases. Flying in restricted airspace is illegal and dangerous.
- Registration Requirements: In many countries, drones must be registered with the relevant aviation authority.
- Operational Limitations: Regulations may limit flight altitude, distance from the pilot, and operational hours.
Potential Hazards and Risk Mitigation, How to operate a drone
Operating a drone involves inherent risks. Understanding these risks and implementing appropriate mitigation strategies is vital for safe drone operation. Potential hazards include collisions with obstacles, loss of control, and battery failure.
- Obstacle Avoidance: Always maintain visual contact with the drone and be aware of surrounding obstacles.
- Emergency Procedures: Be prepared for emergencies, such as sudden battery failure or loss of GPS signal. Know how to perform an emergency landing.
- Weather Awareness: Avoid flying in strong winds, rain, or snow.
Safe Pre-Flight Inspection Flowchart
A visual flowchart simplifies the pre-flight inspection process. This flowchart guides the pilot through each step, ensuring a comprehensive check before takeoff.
(Description of a flowchart: The flowchart would begin with a “Start” node. It would then branch into several steps, including visual inspection of the drone, battery check, GPS signal check, sensor calibration, and weather check. Each step would lead to a “Yes/No” decision point, with “Yes” leading to the next step and “No” leading to troubleshooting or postponing the flight.
The flowchart would conclude with a “Ready for Takeoff” node.)
Taking Off and Landing a Drone

Safe takeoff and landing procedures are fundamental to responsible drone operation. These procedures minimize the risk of accidents and ensure the drone’s safe return to the ground. Different techniques exist, depending on the environment and drone capabilities.
Step-by-Step Takeoff Procedure
A safe takeoff involves a series of steps designed to ensure a smooth and controlled ascent. This minimizes the risk of collisions or loss of control during takeoff.
- Power on the drone and remote controller.
- Wait for the GPS signal to lock.
- Calibrate the compass if needed.
- Perform a pre-flight check of all systems.
- Slowly lift the drone into the air using the control sticks.
- Maintain a steady ascent and hover at a safe altitude.
Takeoff and Landing Techniques
Various techniques exist for takeoff and landing, each suited to different environments and situations. These techniques aim to optimize safety and control during these critical flight phases.
- Normal Takeoff/Landing: A standard vertical ascent and descent.
- Assisted Takeoff/Landing: Using features like GPS assistance for more stable ascents and descents.
- Precision Landing: Utilizing features like waypoint navigation to land in a specific location.
Tips for Smooth Ascents and Descents
Smooth and controlled ascents and descents are crucial for safe drone operation. These tips help minimize the risk of accidents and ensure a safe flight.
- Use gentle and smooth movements of the control sticks.
- Avoid sudden changes in throttle or direction.
- Maintain visual contact with the drone at all times.
- Be aware of wind conditions and adjust your approach accordingly.
Using Different Control Modes
Many drones offer different control modes, each affecting how the drone responds to pilot inputs. Understanding these modes is crucial for safe and effective operation.
- Beginner Mode: Limits the drone’s speed and responsiveness, ideal for new pilots.
- Normal Mode: Provides full control over the drone’s movement.
- Sport Mode: Increases the drone’s responsiveness and speed, for more experienced pilots.
Controlling Drone Movement and Maneuvers
Mastering drone control is essential for safe and effective operation. This involves understanding the functions of the remote control, executing basic maneuvers, and eventually mastering more advanced techniques. This section details the controls and common maneuvers.
Remote Control Functions
A typical drone remote controller has two control sticks and several buttons. Each stick and button performs a specific function, controlling the drone’s movement and features.
- Left Stick: Controls the drone’s yaw (rotation) and altitude.
- Right Stick: Controls the drone’s forward/backward and left/right movement.
- Buttons: Buttons control functions such as camera control, return-to-home (RTH), and flight mode selection.
Basic Drone Maneuvers
Basic maneuvers are fundamental to drone piloting. Mastering these provides a solid foundation for more advanced flight techniques. These maneuvers form the building blocks of more complex aerial operations.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning how to navigate safely and effectively is crucial, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone. This website offers comprehensive guidance on operating a drone responsibly and efficiently, covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques.
Proper drone operation ensures both safety and successful flights.
- Hovering: Maintaining a stable position in the air.
- Moving Forward/Backward: Moving the drone in the direction it is facing.
- Moving Sideways: Moving the drone left or right.
- Rotating: Turning the drone left or right.
Advanced Drone Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers require greater skill and practice. These techniques are useful for specific tasks and enhance the pilot’s overall capabilities.
- Precise Hovering: Maintaining a stable position in challenging conditions.
- Quick Turns: Performing rapid rotations while maintaining stability.
- Flying in Confined Spaces: Navigating through narrow spaces and obstacles.
Common Drone Control Terms
Understanding common drone control terminology is crucial for effective communication and learning. These terms are frequently used in drone piloting manuals and online resources.
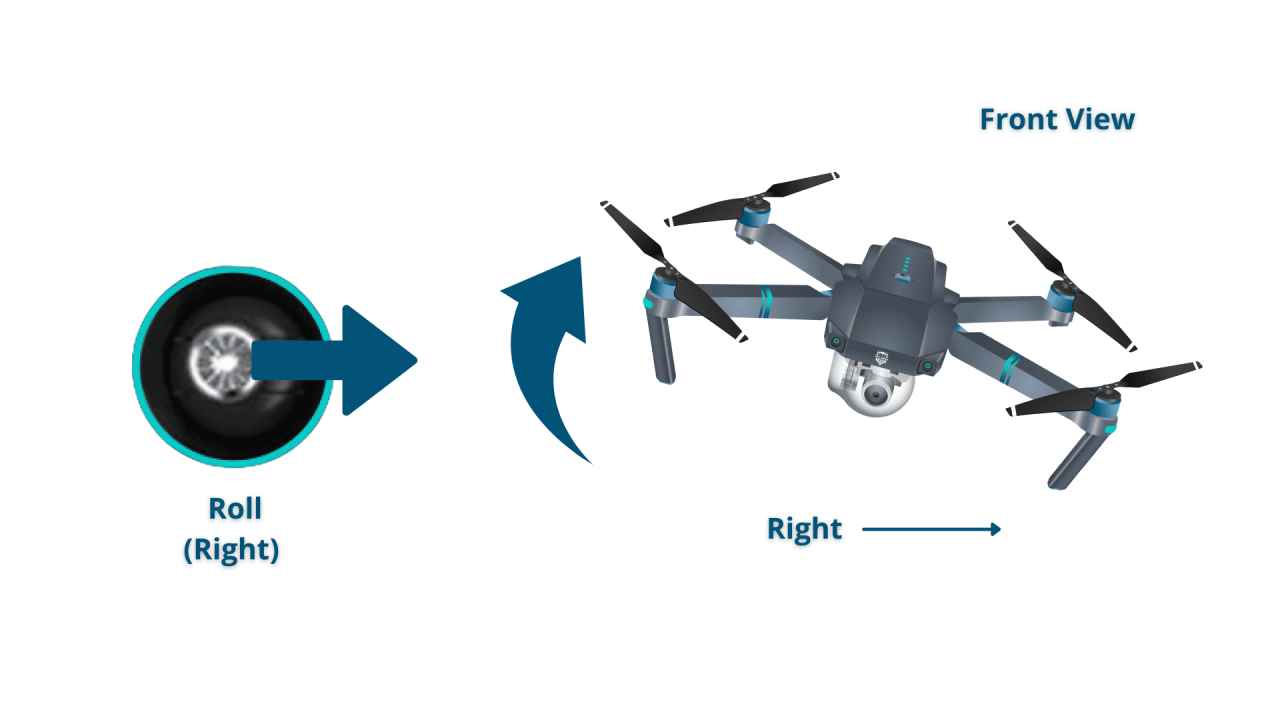
- Yaw: Rotation around the vertical axis.
- Pitch: Movement up or down.
- Roll: Movement left or right.
- Throttle: Control of the drone’s altitude.
- Altitude Hold: Maintaining a constant altitude.
- GPS Mode: Using GPS for position and stability.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
The camera is a key feature of many drones, allowing for stunning aerial photography and videography. Understanding camera settings and composition techniques is essential for capturing high-quality content. This section covers camera settings and techniques for capturing compelling aerial shots.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Camera settings such as ISO, shutter speed, and aperture significantly impact image quality. Adjusting these settings allows for optimal image capture in various lighting conditions.
- ISO: Controls the camera’s sensitivity to light. Higher ISO values are better in low light, but can increase noise.
- Shutter Speed: Determines how long the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds create motion blur.
- Aperture: Controls the size of the lens opening, affecting depth of field. A wider aperture (lower f-stop number) creates a shallow depth of field, blurring the background.
Capturing High-Quality Photos and Videos
Capturing high-quality aerial content requires understanding camera settings and composition techniques. These tips help optimize image quality and visual appeal.
- Use a tripod or gimbal for smooth video footage.
- Experiment with different shutter speeds to capture motion blur or freeze motion.
- Use a wide aperture to create a shallow depth of field.
- Use proper lighting to avoid overexposed or underexposed images.
Composing Compelling Aerial Shots
Aerial photography and videography offer unique perspectives. Effective composition enhances the visual appeal of the captured content. These tips improve the artistic merit of your aerial work.
- Use the rule of thirds to create balanced and visually appealing compositions.
- Use leading lines to guide the viewer’s eye through the image.
- Experiment with different angles and perspectives to create dynamic and interesting shots.
- Consider the lighting and weather conditions when composing your shots.
Different Camera Modes
Most drone cameras offer various modes, each optimized for different types of content creation. Understanding these modes helps in selecting the appropriate settings for specific needs.
- Photo Mode: For capturing still images.
- Video Mode: For capturing moving images.
- Timelapse Mode: For creating time-lapse videos.
- Panorama Mode: For capturing wide-angle panoramic images.
Drone Flight Modes and Features: How To Operate A Drone
Drones offer various flight modes, each designed for specific situations and skill levels. Understanding these modes and their characteristics is crucial for safe and efficient drone operation. This section compares different flight modes and their applications.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, from basic principles to advanced techniques, I recommend checking out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. This will help solidify your understanding of safe and effective drone piloting.
Flight Mode Explanations
Different flight modes offer varying levels of autonomy and control. Each mode is suited to different conditions and pilot experience levels. Selecting the correct mode is crucial for safe and efficient flight.
- GPS Mode: Relies on GPS signals for position and stability, ideal for stable flight and RTH.
- Attitude Mode: Maintains the drone’s attitude (orientation) but doesn’t use GPS for position holding.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): An automated feature that returns the drone to its home point.
- Manual Mode: Provides full manual control over the drone’s movement.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Flight Modes
Each flight mode has advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for specific situations. Understanding these trade-offs helps in choosing the appropriate mode for each flight.
- GPS Mode: Advantages include stability and ease of use; disadvantages include reliance on GPS signal and potential inaccuracy in challenging conditions.
- Attitude Mode: Advantages include responsiveness and maneuverability; disadvantages include lack of position holding and increased risk of losing orientation.
- RTH: Advantages include safety and convenience; disadvantages include potential issues with GPS signal loss or obstacles.
Situational Appropriateness of Flight Modes

The choice of flight mode depends on the specific situation and the pilot’s experience level. Matching the flight mode to the conditions enhances safety and efficiency.
- GPS Mode: Suitable for beginners and stable flights in open areas.
- Attitude Mode: Suitable for experienced pilots and maneuvers requiring precise control.
- RTH: Useful in emergencies or when the drone is out of visual range.
Comparison Table of Flight Modes
| Flight Mode | GPS Dependence | Stability | Maneuverability |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS Mode | High | High | Low |
| Attitude Mode | Low | Low | High |
| RTH | High | Variable | Low |
Mastering drone operation is a rewarding journey that combines technical skill with responsible awareness. This guide has provided a foundational understanding of the key aspects, from pre-flight procedures and flight controls to camera operation and legal compliance. Remember, continuous practice and a commitment to safety are crucial for becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot. Embrace the skies, capture stunning visuals, and always prioritize safety above all else.
Q&A
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS and automated features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with features like Return-to-Home (RTH) and assisted flight modes.
How often should I charge my drone battery?
Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations, but generally, it’s best to charge your drone battery after each use and avoid letting it fully discharge.
What is the range of a typical drone?
Drone range varies greatly depending on the model and environmental conditions. Check your drone’s specifications for its maximum range.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific regulations and registration procedures.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
If possible, engage the Return-to-Home (RTH) function. If RTH fails, try to maintain visual contact and attempt to guide it down safely. Report the incident to the relevant authorities.
